What Are Rotary DIP Switches?
Rotary DIP switches are electromechanical components used for setting or configuring binary values in a device or circuit. They are a type of DIP (Dual Inline Package) switch, which is a manual electrical switch packaged in a small housing with two parallel rows of pins.
The “rotary” aspect of these switches refers to the fact that they are adjusted by rotating a dial or wheel. Each position on the dial corresponds to a specific binary value, allowing users to set different combinations of on/off or high/low states for the switch.
DIP switches, in general, are commonly used for configuration settings in electronic devices. They offer a simple and manual way to set parameters such as address settings, mode selections or other options in a circuit. Rotary DIP switches provide a convenient way to adjust multiple switches simultaneously by rotating a single knob, simplifying the configuration process.
How Does a Rotary DIP Switch Work?
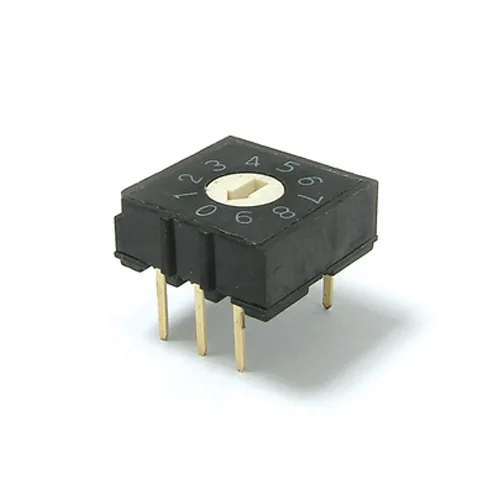

A rotary DIP switch works by providing a set of binary-coded positions corresponding to different settings. Each position on the rotary dial represents a binary value, typically either a 0 or a 1. The switch has a set of contacts arranged in a circular pattern, and as you rotate the dial, these contacts make or break connections to set the desired binary configuration.
Here’s a basic explanation of how a rotary DIP switch works.
#1. Binary Coding: Each position on the rotary dial represents a binary digit (bit). For example, if you have a four-position rotary switch, it can represent a four-bit binary number, allowing 16 possible combinations (2^4).
#2. Internal Structure: Inside the rotary DIP switch, there are wiper contacts that connect with fixed contacts. The arrangement is such that the wiper makes contact with different fixed contacts as the dial is rotated.
#3. Switching States: When the dial is in a specific position, the contacts are configured to represent a binary value. For example, if the switch is set to the third position, it might represent the binary value 0110 (assuming a four-bit switch).
#5. Electrical Connection: Depending on the design, the switch either connects the pins or leaves them disconnected based on the binary configuration. When a pin is connected to the wiper, it carries the electrical signal, and when it’s not connected, the signal is interrupted.
#6. Configuration Setting: The user rotates the dial to the desired position, aligning the contacts to set the specific binary configuration. This manually sets the switch to a particular state.
What Are Rotary DIP Switches Used For?
These switches are often found in various electronic devices, including but not limited to industrial control systems, communication equipment, instrumentation, medical equipment, consumer electronics and the audio/visual market.
Rotary DIP switches are commonly used in situations where manual configuration is necessary, and the binary-coded positions allow for a straightforward way to set various parameters or options in electronic circuits.
Pros & Cons
Pros
Manual Configuration: Rotary DIP switches provide a simple and manual way to configure settings in electronic devices. This can be advantageous in situations where a quick and easy adjustment is needed without the need for external tools or programming interfaces.
Reliability: These switches are generally reliable and have a relatively simple mechanical design. They are less prone to electronic failures compared to more complex electronic components.
Cost: They’re often cost-effective compared to more advanced electronic configuration methods. This can be beneficial for applications with budget constraints.
Physical Feedback: The rotary nature of these switches provides a physical feedback mechanism, allowing users to feel the positions and changes as they rotate the dial. This can aid in ensuring that the correct configuration is set.
Cons
Limited Configurations: They have a limited number of positions, and the number of configurations they can represent is determined by the number of switch positions. This limitation may not be suitable for systems that require a large number of settings.
Space Requirements: The physical size of rotary DIP switches can be a limitation in applications where space is a critical factor. In modern compact electronic devices, alternatives like surface-mount components or a software-based configuration may be preferred.
Limited to Binary Encoding: Rotary DIP switches are typically designed for binary encoding, which may not be optimal for systems that require more complex encoding schemes.
Lack of Remote Configuration: Unlike some electronic configuration methods, rotary DIP switches are limited to manual adjustments. This can be a drawback in applications where remote or automated configuration is necessary.
E-Switch Products
E-Switch offers the following rotary DIP switches: DR Series, RDM Series and RDT Series.